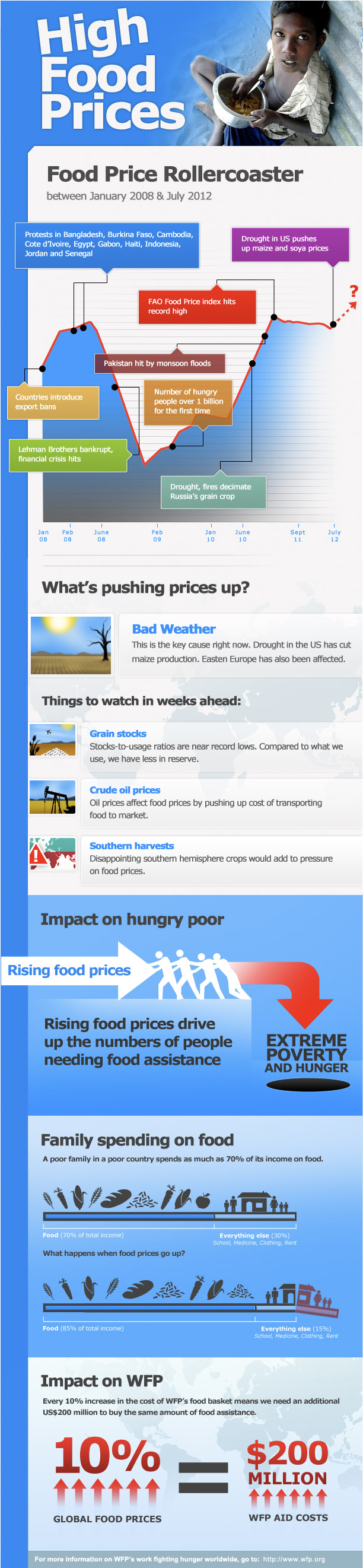
Check out this new infographic from the UN”s World Food Programme which explains how high food prices are affecting the global poor.
Note how some families must spend up to 70% of their income to meet nutritional needs, with the proportion raising up to 85% during times of inflating prices. This means that just 15% of income can be allocated to education, health, and other essential needs. Trade-offs are inevitable.
In Vietnam, food, prices, and hunger are complicated issues. Although many of us would like to think of Vietnam as a country abundant in cheap, delicious foods, the Global Hunger Index actually categorizes Vietnam as having “serious” hunger problems. According to the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI), which produces the Global Hunger Index, an average of 31% of Vietnamese were undernourished between 1990 – 1992. But just as Vietnam has been able to drastically reduce its poverty rates, it’s also been able to reduce the proportion of the population undernourished. Between 1995 – 1997, the average dropped to 22%, then 17% between 2000 – 2002, and 11% between 2005 – 2007.
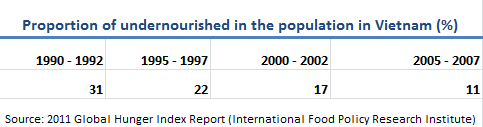
Inflating food prices can also a carry an array of effects on Vietnam’s poor. THE IFPRI noted that increasing prices between 2006 – 2008 could have actually reduced poverty in Vietnam by 8% because the increase food prices benefited many rice farmers, who constitute Vietnam’s rural poor. On the flip side, a recent post on CNBC.com noted that China, Hong Kong, and Vietnam are the three Asian economies most vulnerable to soaring food prices. This, according to economists at Nomura, a financial management consultant firm, is because food prices make up a large portion of Asian countries’ Consumer Price Index (CPI), a measure that weighs the average price of basic goods for a consumer.
Tai Hui, a head economist at the Regional Research for Asia with Standard Chartered, explained to CNBC that China, Hong Kong, Vietnam are particularly vulnerable to food inflation because their CPI baskets are highly correlated with global prices as measured by the CBR/Reuters Food Index, which have been increasing in the past three months: “Hui said for every one percentage point increase in the CRB Food Index, inflation in Vietnam, and China and Hong Kong goes up 13.7 basis points, 6.3 basis points and 4.9 basis points, respectively.”
For now, though, hunger in these three economies has not hit crisis levels. We’re hoping it remains that way–and gets better.